update: 2015/11/12
reference:
1. Professional CUDA C Programming
2. I touchs: Get Started On NVIDIA Jetson TK1
3. I touchs: How to re-flash your Jetson TK1 Development Kit
4. I touchs: Using the Jetson TK1 as a remote development environment for CUDA
5. CUDA Runtime API :: CUDA Toolkit Documentation
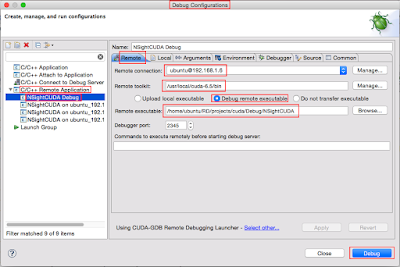
A. 在 Nsight Eclipse Edition 撰寫程式如下:
// 檔名: checkDeviceInfor.cu
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/*
* Display a variety of information on the first CUDA device in this system,
* including driver version, runtime version, compute capability, bytes of
* global memory, etc.
*/
void CHECK(cudaError_t call)
{
const cudaError_t error = call;
if (error != cudaSuccess)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s:%d, ", __FILE__, __LINE__);
fprintf(stderr, "code: %d, reason: %s\n", error,
cudaGetErrorString(error));
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
printf("\n%s Starting...\n\n", argv[0]);
int deviceCount = 0;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&deviceCount);
if (deviceCount == 0)
{
printf("There are no available device(s) that support CUDA\n");
}
else
{
printf("Detected %d CUDA Capable device(s)\n", deviceCount);
}
int dev = 0, driverVersion = 0, runtimeVersion = 0;
CHECK(cudaSetDevice(dev));
cudaDeviceProp deviceProp;
CHECK(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProp, dev));
printf("Device %d: \"%s\"\n\n", dev, deviceProp.name);
cudaDriverGetVersion(&driverVersion);
cudaRuntimeGetVersion(&runtimeVersion);
printf(" CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version %d.%d / %d.%d\n",
driverVersion / 1000, (driverVersion % 100) / 10,
runtimeVersion / 1000, (runtimeVersion % 100) / 10);
printf(" CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: %d.%d\n\n",
deviceProp.major, deviceProp.minor);
printf(" Total amount of global memory: %.2f MBytes (%llu "
"bytes)\n", (float)deviceProp.totalGlobalMem / pow(1024.0, 3),
(unsigned long long)deviceProp.totalGlobalMem);
printf(" GPU Clock rate: %.0f MHz (%0.2f "
"GHz)\n", deviceProp.clockRate * 1e-3f,
deviceProp.clockRate * 1e-6f);
printf(" Memory Clock rate: %.0f Mhz\n",
deviceProp.memoryClockRate * 1e-3f);
printf(" Memory Bus Width: %d-bit\n",
deviceProp.memoryBusWidth);
if (deviceProp.l2CacheSize)
{
printf(" L2 Cache Size: %d bytes\n\n",
deviceProp.l2CacheSize);
}
printf(" Max Texture Dimension Size (x,y,z) 1D=(%d), "
"2D=(%d,%d), 3D=(%d,%d,%d)\n", deviceProp.maxTexture1D,
deviceProp.maxTexture2D[0], deviceProp.maxTexture2D[1],
deviceProp.maxTexture3D[0], deviceProp.maxTexture3D[1],
deviceProp.maxTexture3D[2]);
printf(" Max Layered Texture Size (dim) x layers 1D=(%d) x %d, "
"2D=(%d,%d) x %d\n\n", deviceProp.maxTexture1DLayered[0],
deviceProp.maxTexture1DLayered[1], deviceProp.maxTexture2DLayered[0],
deviceProp.maxTexture2DLayered[1],
deviceProp.maxTexture2DLayered[2]);
printf(" Total amount of constant memory: %lu bytes\n",
deviceProp.totalConstMem);
printf(" Total amount of shared memory per block: %lu bytes\n",
deviceProp.sharedMemPerBlock);
printf(" Total number of registers available per block: %d\n\n",
deviceProp.regsPerBlock);
printf(" Warp size: %d\n\n",
deviceProp.warpSize);
printf(" Maximum number of threads per multiprocessor: %d\n",
deviceProp.maxThreadsPerMultiProcessor);
printf(" Maximum number of threads per block: %d\n",
deviceProp.maxThreadsPerBlock);
printf(" Maximum sizes of each dimension of a block: %d x %d x %d\n",
deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[0],
deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[1],
deviceProp.maxThreadsDim[2]);
printf(" Maximum sizes of each dimension of a grid: %d x %d x %d\n",
deviceProp.maxGridSize[0],
deviceProp.maxGridSize[1],
deviceProp.maxGridSize[2]);
printf(" Maximum memory pitch: %lu bytes\n\n",
deviceProp.memPitch);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
B. 執行結果:
C. 備註:
還可以使用 command-line 的工具: nvidia-smi (System Management Interface),
不過 Jetson TK1 似乎不支援.